Difference between revisions of "LipidXplorer Principles"
(Created page with '==The Workflow of LipidXplorer== 600px|center|LipidXplorer Workflow The working of LipidXplorer can be depicted as a simple workflow scheme. The...') |
Shevchenko (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | ==The Workflow of LipidXplorer== | + | == The Workflow of LipidXplorer == |
| − | [[Image:LipidX-Workflow.png|600px | + | [[Image:LipidX-Workflow.png|center|600px|LipidXplorer Workflow]] |
| − | + | <br> | |
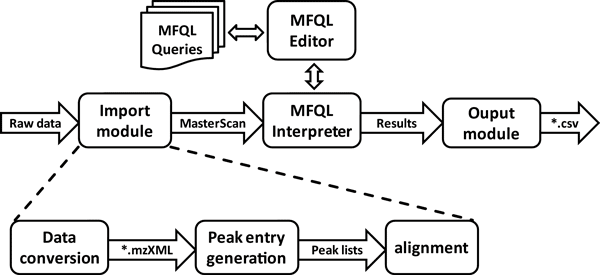
| − | + | Shotgun MS and MS/MS spectra can be acquired at any mass spectrometer and submitted in .mzXML file format. Alternatvely, the Import module can automatically convert files from .raw (used by Thermo Fisher Scientific) or .wiff (used by AB Sciex) acquisiton software. Spectra are aligned and stored in the MasterScan, in which lipids are identified. The Molecular Fragmentation Query Language (MFQL) Interpreter applied user-defined lipid-class and / or lipid species specific queries, written in molecualr fragmentation query (MFQL) language using MFQL Editor for probing the MasterScan. The identified lipids and intensities of user-defined reporter ions (molecualr ions of intact precursors or of any specific fragments) are reported by Ouput module as a *.csv file. | |
| − | file format ( | ||
| − | the MasterScan. The | ||
| − | Molecular Fragmentation Query Language (MFQL) Interpreter | ||
| − | |||
| − | The | ||
| − | |||
| − | ==The MasterScan database== | + | == The MasterScan database == |
| − | + | The MasterScan flat file database contains is built from all MS and MS/MS spectra acquired during the entire series of experiments, including all control samples and technical or biological replicas. The spectra are then aligned and MS/MS spectra associated to correspondent precursors and also aligned.Notye that the database size is strngly reduced comapared to the bulk of original raw spectra, because MasterScan only stores the representative masses of aligned and merged peaks (but not each mass detected in each spectrum). However, peak intentsities in each indiidual acquisition are preserved.<br> | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | technical | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | [[Image:MasterScan.png|center|600px|MasterScan]] | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
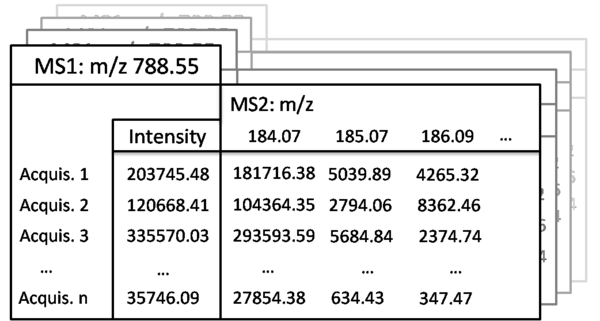
| − | + | The MasterScan is schematically depicted here as file cabinet addressed at the top-level by the precursor masses (MS1) while intensities are assigned to each acquisition (Acquis.). In this example the precursor mass is m/z 788.55 and n samples are present. If MS2 experiments were acquired a list of fragment masses is linked to their precursor mass and intensities are assigned for each acquisition. In this example MS2 peaks of m/z 184.07, m/z 185.07 and m/z 788.55 are shown with their intensities for each acquisition (Acquis.). | |
| − | + | ||
| + | == Molecular Fragmentation Query Language<br> == | ||
| + | |||
| + | Query languages are computer languages used to make queries into databases and information systems (see [[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Query_language Wikipedia: Query language]]) | ||
| + | |||
| + | To the best of our knowledge, this is first application of a query language for identifying lipids in mass spectra. MFQL queries are definded by the user by formalizing compositional restrictions or fragmentation pathways known or assumed for lipids of any given class. Multiple repoter ions could be used for identifying species of a lipid class. MasterScan can be probed by virstully unlimited number of MFQL queiries in parallel, while no dataset modification or changing the processing settings are required. Further details on the structure and syntaxis of MFQL is provided in the corresponding section of this tutorial<br> | ||
Revision as of 00:59, 2 February 2011
The Workflow of LipidXplorer
Shotgun MS and MS/MS spectra can be acquired at any mass spectrometer and submitted in .mzXML file format. Alternatvely, the Import module can automatically convert files from .raw (used by Thermo Fisher Scientific) or .wiff (used by AB Sciex) acquisiton software. Spectra are aligned and stored in the MasterScan, in which lipids are identified. The Molecular Fragmentation Query Language (MFQL) Interpreter applied user-defined lipid-class and / or lipid species specific queries, written in molecualr fragmentation query (MFQL) language using MFQL Editor for probing the MasterScan. The identified lipids and intensities of user-defined reporter ions (molecualr ions of intact precursors or of any specific fragments) are reported by Ouput module as a *.csv file.
The MasterScan database
The MasterScan flat file database contains is built from all MS and MS/MS spectra acquired during the entire series of experiments, including all control samples and technical or biological replicas. The spectra are then aligned and MS/MS spectra associated to correspondent precursors and also aligned.Notye that the database size is strngly reduced comapared to the bulk of original raw spectra, because MasterScan only stores the representative masses of aligned and merged peaks (but not each mass detected in each spectrum). However, peak intentsities in each indiidual acquisition are preserved.
The MasterScan is schematically depicted here as file cabinet addressed at the top-level by the precursor masses (MS1) while intensities are assigned to each acquisition (Acquis.). In this example the precursor mass is m/z 788.55 and n samples are present. If MS2 experiments were acquired a list of fragment masses is linked to their precursor mass and intensities are assigned for each acquisition. In this example MS2 peaks of m/z 184.07, m/z 185.07 and m/z 788.55 are shown with their intensities for each acquisition (Acquis.).
Molecular Fragmentation Query Language
Query languages are computer languages used to make queries into databases and information systems (see [Wikipedia: Query language])
To the best of our knowledge, this is first application of a query language for identifying lipids in mass spectra. MFQL queries are definded by the user by formalizing compositional restrictions or fragmentation pathways known or assumed for lipids of any given class. Multiple repoter ions could be used for identifying species of a lipid class. MasterScan can be probed by virstully unlimited number of MFQL queiries in parallel, while no dataset modification or changing the processing settings are required. Further details on the structure and syntaxis of MFQL is provided in the corresponding section of this tutorial